As we all know that the clarity of the ultrasound image determines whether our diagnosis is accurate, In addition to the performance of the machine, we actually have other ways to improve the clarity of the image.
In addition to what we mentioned in the previous article, the following factors will affect ultrasound images.
1. Resolution
There are three major resolutions of ultrasound: spatial resolution, time resolution, and contrast resolution.
● Spatial resolution
Spatial resolution is the ability of ultrasound to distinguish two points at a specific depth, divided into axial resolution and lateral resolution.
Axial resolution is the ability to distinguish between two points in a direction parallel to the ultrasound beam (longitudinal), and is proportional to transducer frequency.
The axial resolution of the high-frequency probe is high, but at the same time the attenuation of the sound wave in the tissue is also greater, which will result in a high axial resolution of the shallow structure, while the axial resolution of the deep structure is relatively low, so I want to improve Axial resolution of deep structures, either by bringing high-frequency transducers close to the target (eg, transesophageal echocardiography) or by switching to low-frequency transducers. This is why it is recommended to use high-frequency probes for superficial tissue ultrasound and low-frequency probes for deep tissue ultrasound.
Lateral resolution is the ability to distinguish two points perpendicular to the direction of the ultrasonic beam (horizontal). In addition to being proportional to the frequency of the probe, it is also closely related to the setting of the focus. The width of the ultrasonic beam is the narrowest in the focus area, so Lateral resolution is best at focus. Above we can see that the frequency and focus of the probe are closely related to the spatial resolution of ultrasound.1
Figure 1
● Temporal resolution
Temporal resolution, also known as frame rate, refers to the number of frames per second of imaging. Ultrasound is transmitted in the form of pulses, and the next pulse can only be transmitted after the previous pulse returns to the ultrasound probe.
The time resolution is negatively correlated with the depth and the number of focal points. The greater the depth and the more focal points, the lower the pulse repetition frequency and the lower the frame rate. The slower the imaging, the less information captured in a short period of time. Usually when the frame rate is below 24 frames/s, the image will flicker.
During clinical anesthesia operations, when the needle moves rapidly or the drug is injected rapidly, the low frame rate will cause blurred images, so temporal resolution is very important for the visualization of the needle during puncture.
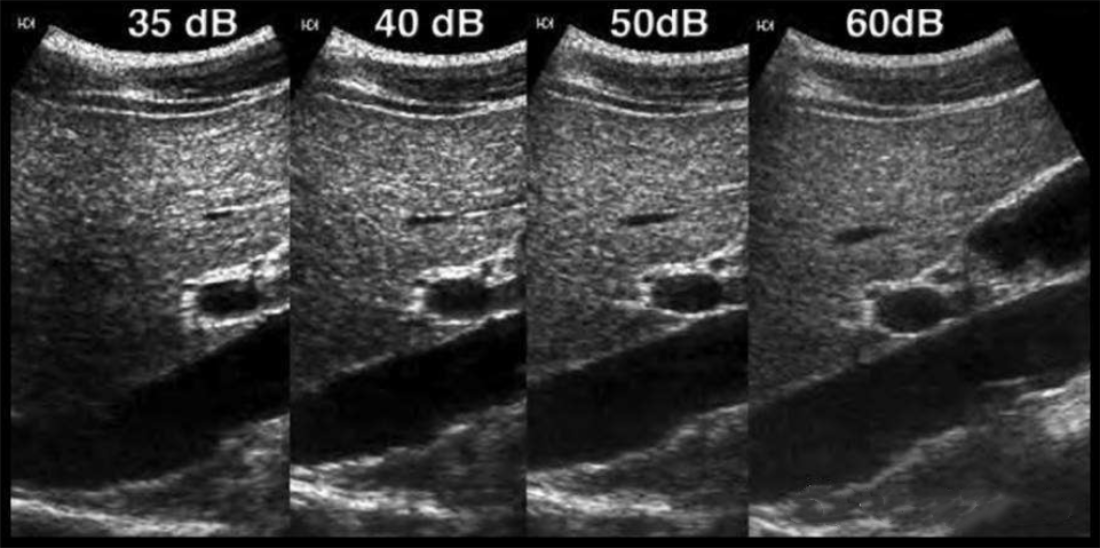
Contrast resolution refers to the smallest gray scale difference that the instrument can distinguish. Dynamic range is closely related to contrast resolution, the larger the dynamic range, the lower the contrast, the smoother the image, and the higher the ability to identify two similar tissues or objects (Figure 2).
Figure 2
2.Frequency
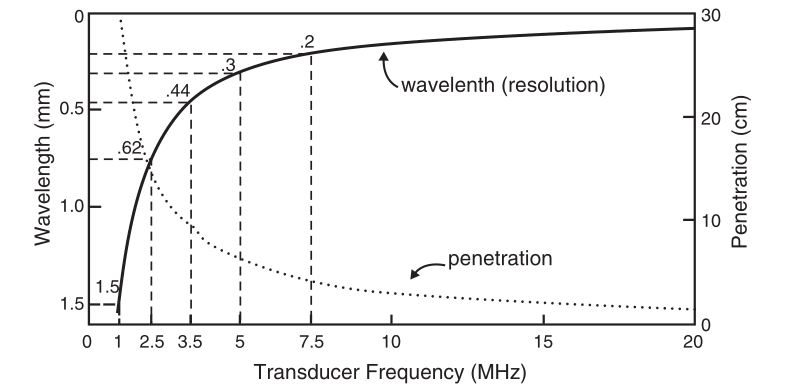
Frequency is directly proportional to spatial resolution and inversely proportional to ultrasound penetration (Figure 3). High frequency, short wavelength, large attenuation, poor penetration, and high spatial resolution.
Figure 3
In clinical work, the targets of most operations are relatively superficial, so high-frequency linear array probes can meet the daily operational needs of doctors, but when encountering obese patients or deep puncture targets (such as lumbar plexus), A low frequency convex array probe is also essential.
Most of the current ultrasonic probes are broadband, which is the basis for realizing frequency conversion technology. Frequency conversion means that the working frequency of the probe can be changed when using the same probe. If the target is superficial, select a high frequency; if the target is deep, select a low frequency.
Taking Sonosite ultrasound as an example, its frequency conversion has 3 modes, namely Res (resolution, will provide the best resolution), Gen (general, will provide the best balance between resolution and penetration), Pen (penetration, will provide the best penetration). Therefore, in actual work, it needs to be adjusted according to the depth of the target area.
Post time: Jul-10-2023